G7 pledges joint effort on AI adoption
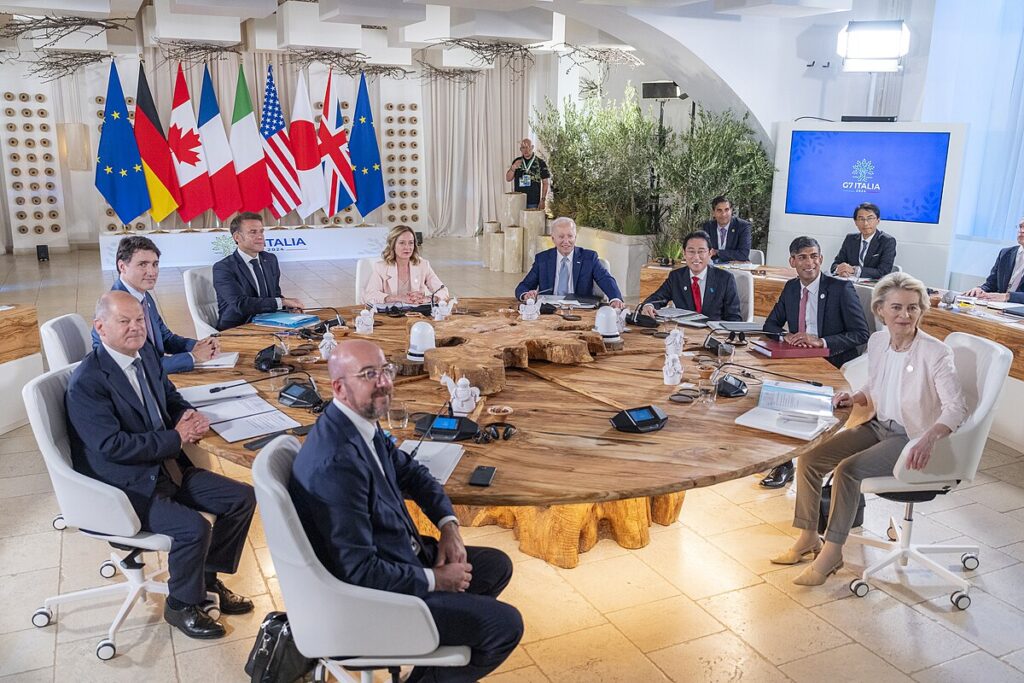
Leaders at the G7 Summit have pledged a joint effort to accelerate the adoption of artificial intelligence across various sectors. Recognising the transformative potential of AI technology, the G7 nations are committed to working together to boost its integration within the public sector. This initiative aims to improve efficiency, enhance services, and foster innovation across government operations.
A key priority is supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in their digital transformation journey. The G7 recognises that SMEs often face unique challenges in accessing and implementing AI solutions. Therefore, the focus will be on helping SMEs adopt and develop safe, secure, and trustworthy AI systems, ensuring they can benefit from this technology and remain competitive in the global market. This cooperation will facilitate the sharing of best practices and resources, empowering SMEs to leverage AI for growth and efficiency.
The G7 also acknowledges the significant energy demands associated with AI. A crucial aspect of their joint effort involves addressing these energy challenges and exploring the potential of AI in driving energy efficiency and innovation. This includes developing AI-powered solutions for optimising energy consumption, improving grid management, and accelerating the development of renewable energy sources. By harnessing AI, the G7 aims to create a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
Key Areas Of Collaboration
The G7 nations are set to intensify their cooperation in several key areas to drive responsible artificial intelligence development and deployment. One primary focus is on establishing common standards and frameworks for AI, ensuring interoperability and facilitating cross-border data flows. This collaborative approach will promote a level playing field for businesses and researchers, encouraging innovation and preventing fragmentation of the global AI landscape. Harmonising regulations and guidelines is crucial for fostering trust and confidence in AI technology.
Another vital area of collaboration centres on promoting AI skills development and education. The G7 recognises the need to equip the workforce with the necessary skills to thrive in an AI-driven economy. This involves investing in education and training programmes that focus on AI-related skills, such as data science, machine learning, and AI ethics. By fostering a skilled workforce, the G7 aims to ensure that its citizens can fully participate in and benefit from the digital transformation powered by AI.
Furthermore, the G7 is committed to supporting research and development in AI, particularly in areas that address societal challenges. This includes funding research into AI applications for healthcare, climate change, and sustainable development. By pooling resources and expertise, the G7 nations can accelerate the development of innovative AI solutions that contribute to solving pressing global issues. This collaborative approach to research and development will help unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence for the benefit of humanity.
Addressing Ai Risks
Recognising the potential risks associated with artificial intelligence, the G7 is committed to addressing these challenges proactively. A key focus is on mitigating biases in AI systems to ensure fairness and prevent discrimination. The G7 nations will work together to develop methodologies for identifying and rectifying biases in AI algorithms and datasets. This collaborative effort aims to promote equitable outcomes and prevent the perpetuation of societal inequalities through AI technology. Ensuring transparency and accountability in AI systems is also vital to build public trust and confidence.
Another critical area involves addressing cybersecurity threats related to AI. As AI systems become more integrated into critical infrastructure and sensitive applications, protecting them from malicious attacks is paramount. The G7 will collaborate on developing robust cybersecurity frameworks and best practices for AI, including measures to prevent data breaches, algorithmic manipulation, and other forms of cybercrime. Strengthening international cooperation on cybersecurity is essential to safeguard the integrity and reliability of AI systems. This includes promoting information sharing and joint exercises to enhance preparedness and response capabilities.
The G7 also acknowledges the importance of addressing the potential misuse of AI for malicious purposes, such as autonomous weapons and surveillance technologies. They are committed to working together to establish ethical guidelines and legal frameworks that govern the development and deployment of AI in these sensitive areas. This includes promoting responsible innovation and preventing the use of AI in ways that violate human rights or undermine international security. The G7’s cooperation aims to ensure that AI technology is used for the benefit of humanity and not as a tool for harm.
Global Ai Governance
The G7 nations recognise that the governance of artificial intelligence requires a global perspective. They are dedicated to fostering international cooperation to establish common principles and standards for AI governance. This includes working with international organisations, such as the United Nations and the OECD, to promote a harmonised approach to AI regulation and ethics. By engaging in multilateral dialogue, the G7 aims to ensure that AI is developed and deployed responsibly on a global scale, addressing concerns related to data privacy, security, and human rights. This collaborative effort is essential for building a trusted and inclusive AI ecosystem.
A central aspect of global AI governance is promoting interoperability and avoiding fragmentation. The G7 seeks to facilitate the seamless flow of data and AI technologies across borders, while respecting national laws and regulations. This involves establishing common frameworks for data governance, including data protection and cross-border data transfers. By fostering interoperability, the G7 aims to unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence for global innovation and economic growth. This also requires addressing potential barriers to trade and investment in AI, such as discriminatory practices and protectionist measures.
Furthermore, the G7 recognises the importance of promoting ethical considerations in AI development and deployment worldwide. This includes establishing ethical guidelines and frameworks that address issues such as bias, fairness, and accountability. The G7 nations will work together to promote responsible innovation in AI, ensuring that the technology is used for the benefit of all and does not exacerbate existing inequalities. By championing ethical AI, the G7 aims to build public trust and confidence in this transformative technology and promote its responsible adoption across the globe. This requires ongoing dialogue and collaboration with stakeholders, including governments, industry, academia, and civil society.